MCT Oil vs Exogenous Ketones: Which Is Better for Energy & Fat Loss?
Choosing between MCT oil and exogenous ketones can be confusing. Both are promoted for increasing energy, supporting ketosis, and accelerating fat loss — but they function very differently inside the body.
MCT oil encourages your liver to produce its own ketones, leading to steadier energy and metabolic support. Exogenous ketones, on the other hand, raise blood ketone levels directly, creating a faster but shorter-lived effect.

If you’re following a ketogenic or low-carb approach, understanding how each supplement works can help you decide which aligns with your goals — whether that’s sustained fat adaptation, workout performance, or mental clarity.
Before relying on supplements, it’s also important to ensure your foundational keto structure is correct, since execution mistakes often limit results more than product choice.
Key Takeaways
- MCT oil encourages your body’s own ketone production for steady energy and fat metabolism
- Exogenous ketones give you an instant energy boost and can smooth out that rough keto transition
- The best pick depends on your goals, daily habits, and how your body reacts
What Are MCT Oil and Exogenous Ketones?

MCT oil and exogenous ketones both help with energy and fat metabolism, but they do it differently. They change the way your body makes and uses ketones—those little fuel molecules that kick in when carbs are low.
Defining MCT Oil
MCT oil stands for medium-chain triglyceride oil. Usually, it’s made from coconut or palm kernel oil, and it’s packed with fatty acids containing 6–12 carbon atoms. These medium chains make MCTs way easier to digest than the long-chain fats you find in most foods.
Once you take MCTs, they head straight to your liver, where they’re turned into ketones pretty quickly. Those ketones can fuel your brain and muscles, even if you haven’t had carbs in a while.
People use MCT oil to stay in ketosis, when your body runs on fat. It also helps cut down hunger and keeps your energy more stable between meals. Not bad, right?
Common types of MCTs include:
- C8 (caprylic acid): Converts to ketones the fastest
- C10 (capric acid): Gives balanced energy
- C12 (lauric acid): Digests slower but helps your immune system
Because it turns into energy so fast, MCT oil is a favorite in keto coffee, shakes, or smoothies.
If you’re new to the keto lifestyle, our Beginner’s Guide to Ketogenic Diet breaks down how your body transitions into fat-burning mode
Understanding Exogenous Ketones
Exogenous ketones are ketone bodies made outside your body and taken as supplements. You’ll usually see them as ketone salts or ketone esters. Both types bump up your blood ketone levels right away, skipping the fat-burning step.
They’re designed to copy the effects of endogenous ketones—the kind your body makes during fasting or carb restriction. By raising ketones, they can give you a quick energy burst for your brain or muscles.
Some folks use them to make starting keto less miserable (goodbye, keto flu). Others take them before hitting the gym for a fast fuel-up.
The catch? The effects don’t last long, and you don’t get all the perks of sticking to a real ketogenic diet.
Key Differences Between MCT Oil and Exogenous Ketones
They both make more ketones available, but the way they do it couldn’t be more different. MCT oil gets your body to make ketones, while exogenous ketones just give them to you.
| Feature | MCT Oil | Exogenous Ketones |
|---|---|---|
| Source | From coconut or palm oil | Made in labs |
| How it works | Boosts your liver’s ketone production | Directly raises blood ketones |
| Duration of effect | Steady, longer energy | Fast but short-lived |
| Common use | Everyday energy and fat burning | Quick boost or keto adaptation |
MCT oil is more about keeping your energy and fat-burning steady, while exogenous ketones are a short-term hack for performance or getting through keto’s rough patches.
How They Work: Mechanisms for Energy and Fat Loss
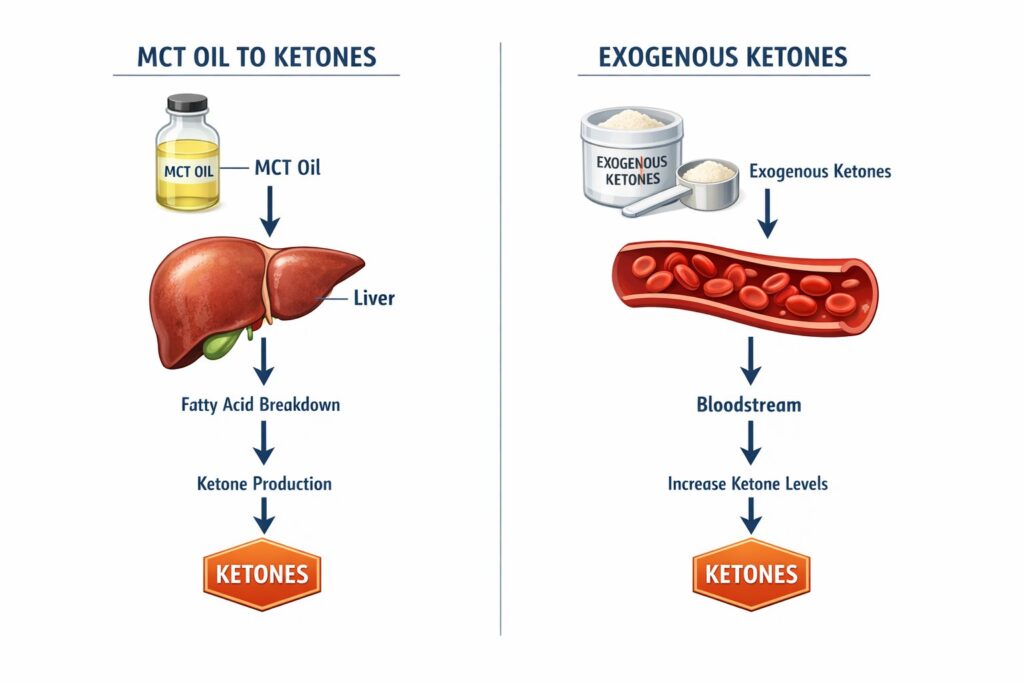
Both MCT oil and exogenous ketones up your ketone supply, which your body can use for energy when you’re low on glucose. But they go about it in their own way, and their effects on fat burning and energy aren’t identical.
MCT Oil and Ketone Production
MCTs are fats that get absorbed and burned pretty fast. Unlike regular fats, they shoot straight to your liver via the portal vein and turn into ketone bodies like beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) and acetoacetate.
This process—ketogenesis—ramps up your own ketone production, even if you’re not super low on carbs. Since MCTs are burned for energy quickly, they’re less likely to end up as body fat.
MCT oil can help you stay in mild ketosis and keep your brain and muscles fueled. It might also give your metabolism a tiny nudge, which could help with fat loss if you’re eating right.
Main effects of MCT oil:
- Kicks off your body’s ketone production
- Gives quick, usable energy
- Mildly boosts fat burning
Exogenous Ketones and Direct Ketosis
Exogenous ketone supplements put ketones straight into your bloodstream, usually as BHB salts or ketone esters. This skips the liver and gives you a quick spike in blood BHB levels.
By flooding your system with ketones, they can kind of mimic fasting or keto—at least for a bit. Your brain, heart, and muscles will use these ketones instead of glucose.
But here’s the thing: exogenous ketones don’t really make you burn more fat, since you’re just adding outside energy. They might help curb your appetite and keep blood sugar steady, but real fat loss still comes down to what you eat and how much you move.
Common forms:
| Type | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Ketone salts | BHB with minerals | Moderate, doesn’t last long |
| Ketone esters | Pure BHB | Stronger, lasts a bit longer |
Impact on Metabolism and Fat Burning
Both MCTs and exogenous ketones push your body to use ketones instead of glucose for energy. This can make you more efficient, especially during endurance workouts or if you’re low-carb.
MCT oil encourages your body to burn its own stored fat, while exogenous ketones mostly just give you a ready energy source—they might help you save some muscle glycogen during exercise.
MCTs can bump up your calorie burn a little, but exogenous ketones mostly change what fuel your body uses, not how much you burn. In the end, your results depend on your diet, exercise, and how you use these supplements.
Benefits of MCT Oil for Energy and Weight Management

MCT oil is a fast energy source, helps with brain function, and might even help keep your hunger in check. It turns into ketones quickly, which is why so many keto and low-carb folks use it to keep their energy up and manage weight.
Rapid Energy Boost and Mental Clarity
MCT oil is loaded with medium-chain triglycerides—mostly caprylic (C8) and capric (C10) acids—that your liver turns into ketones. These ketones fuel both your muscles and your brain.
Unlike regular fats, MCTs skip the usual digestion steps and hit your bloodstream fast. That means you get mental clarityand focus, especially if you’re fasting or eating very few carbs. Some people swear by adding MCT oil to coffee or smoothies for better concentration, minus the sugar rush.
Since ketones are a solid fuel for your brain, MCT oil might help you avoid that afternoon fog. It’s popular with folks who need steady energy for work, studying, or workouts.
Support for Ketogenic and Low-Carb Diets
If you’re on a keto diet, MCT oil helps you stay in ketosis—that fat-burning state. When you take MCTs, your blood ketone levels go up, so you’ve got energy even if you’re barely eating carbs.
MCT oil is a go-to for keto recipes and fat bombs since it gives you fast fuel without kicking you out of ketosis. It can also help with that early keto fatigue a lot of people get.
Because your body absorbs it so quickly, MCT oil works before workouts or during fasting to keep your stamina up. It’s helpful for keeping energy steady and may make the “keto flu” less of a hassle.
Appetite Control and Weight Loss Effects
MCT oil might help with weight management by making you feel fuller and cutting down on cravings. Some studies say MCTs boost hormones like peptide YY and leptin, which help control appetite.
Swapping out other fats for MCT oil can also raise your calorie burn a little, thanks to its thermogenic effect—your body uses more energy to digest it. This could help with slow and steady weight loss if you’re eating well and staying active.
People often add MCT oil to their morning drinks or meals to help with hunger during intermittent fasting. It’s a handy way to get quick energy and curb cravings, making it a practical option for long-term weight management.
Learn more about Hidden Carbs That Can Sabotage Your Keto Diet to keep your fat loss on track.
Benefits of Exogenous Ketones for Energy and Fat Loss

Exogenous ketones give your body an outside source of ketones. This can raise blood ketone levels, make energy more available, and help with fat metabolism.
They might also keep your mind sharp and help cut down on tiredness, especially during low-carb eating or fasting. It’s a handy shortcut when your energy dips.
Immediate Elevation of Blood Ketone Levels
Exogenous ketones—like ketone salts and ketone esters—push ketones straight into your blood. Usually, this bumps up blood ketone levels in about 30 to 60 minutes.
That quick spike gives you another fuel option when glucose is running low, like if you’re fasting or skipping carbs. Unlike MCT oil, which your liver has to process, exogenous ketones work almost right away.
Some folks use these before a workout or when they hit an afternoon slump, looking for a fast, noticeable boost. It’s not permanent—maybe a few hours—but it can help fill in the gaps while your body gets used to burning fat for fuel.
In many cases, what feels like low energy during keto is actually related to electrolyte imbalance rather than insufficient ketone production.
| Type | Absorption Speed | Duration of Effect | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketone Salts | Moderate | 2–3 hours | Daily energy or mental focus |
| Ketone Esters | Fast | 3–5 hours | Athletic performance or research use |
Enhancing Performance and Cognitive Function
More ketones in your blood can sharpen mental clarity and focus. The brain runs surprisingly well on ketones, especially if you’re new to keto and feeling a bit foggy from low glucose.
Athletes and active people sometimes notice steadier energy from exogenous ketones. They can help you rely less on glycogen and push through longer workouts.
Some research points to ketone esters improving time-to-exhaustion and lowering how hard exercise feels. Not everyone gets the same results, but a lot of folks say their energy feels smoother and their mind stays clearer than when they’re just eating carbs.
Role in Fasting and Ketosis Maintenance
During fasting or intermittent fasting, exogenous ketones can keep your energy up and hunger down. They give a little bit of fuel without knocking you out of ketosis.
If you slip up and eat some extra carbs, exogenous ketones can act as a buffer. They help keep you in ketosis even when things aren’t totally perfect.
However, understanding where you are in your keto adaptation timeline matters more than using supplements to compensate for dietary inconsistencies.
Some people find that taking exogenous ketones during fasting helps them concentrate and stay productive. That steady brain energy can make fasting less of a struggle and maybe even stretch your fasting window a bit longer.
Types and Sources: MCT Oil and Exogenous Ketones Compared

MCT oil and exogenous ketones aren’t quite the same thing. MCT oil has special fats that your liver turns into ketones, while exogenous ketones are basically ready-to-go ketones in supplement form.
Their sources and chemical details change how well they support your energy and fat metabolism. It’s not always obvious which one will work best for you until you try them.
Fatty Acid Composition in MCT Oil
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are fats with 6–12 carbon atoms. The main players are caproic acid (C6), caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), and lauric acid (C12).
C8 MCT oil (caprylic acid) converts to ketones faster than the others, so it’s popular for quick energy. Capric acid (C10)helps too, just not as quickly. Lauric acid (C12) digests more slowly, acting more like a long-chain fat and giving a longer-lasting effect.
You’ll find MCTs in coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and sometimes butter. Coconut oil is about 55–65% MCTs, but only a little is pure C8 or C10. If you want the fast stuff, refined MCT oil supplements are the way to go.
| Fatty Acid | Carbon Length | Common Name | Conversion Speed to Ketones |
|---|---|---|---|
| C8 | Caprylic acid | Very fast | High |
| C10 | Capric acid | Fast | Moderate |
| C12 | Lauric acid | Slower | Low |
Forms of Exogenous Ketone Supplements
Exogenous ketones mainly come as ketone salts or ketone esters. Both boost blood ketones, but your body handles them a bit differently.
Ketone salts are beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) combined with minerals like sodium, calcium, or magnesium. They’re easier to take and taste better, but too much can bother your stomach.
Ketone esters are BHB linked to an alcohol molecule. They’re stronger and work faster, but wow—they taste bitter and can get pricey. Esters might be best for athletes or anyone needing a fast mental or physical jolt, while salts are more for everyday use.
| Type | Composition | Effect Duration | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketone Salts | BHB + Minerals | Moderate | Daily support |
| Ketone Esters | BHB + Alcohol | Short but strong | Performance boost |
Natural vs Supplemental Sources
MCT oil is found in nature—think coconut oil, palm oil, and butter—so you can get it from your regular food. MCT oil supplements just concentrate the most useful fatty acids for a quicker effect.
But exogenous ketones are synthetic. Your body doesn’t make them from food—they come from labs, packaged as powders, drinks, or capsules. They give you instant ketones, but they don’t replace your body’s own fat-burning process.
Natural sources give you a slower, steadier effect, while supplements offer speed. It really comes down to whether you want a gentle, ongoing boost or a quick shot of ketones.
Side Effects and Safety Considerations

MCT oil and exogenous ketones can both mess with your stomach if you take too much or don’t give your body time to adjust. Everyone’s tolerance is different, so it’s smart to start slow and see how you feel.
Digestive Issues and Tolerance
MCT oil is kind of famous for causing gastrointestinal symptoms—especially if you take more than a tablespoon at once. You might get diarrhea, stomach discomfort, bloating, or nausea. It’s because MCTs are absorbed super fast, and sometimes your gut just isn’t ready for it.
Most people start with 1 teaspoon per day and work their way up. Mixing it into food can help keep things calm.
Exogenous ketones, whether salts or esters, can cause similar issues. Some folks get gas or cramping if they take them on an empty stomach. Drinking extra water and splitting up your doses can make a difference.
| Common Digestive Reactions | Possible Cause | Suggested Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhea | Excess MCT intake | Reduce serving size |
| Nausea | Rapid absorption | Take with food |
| Bloating | Ketone salts | Split doses through the day |
Potential Adverse Reactions
Taking a lot of MCT oil means you’re adding more saturated fats to your diet. If you’re watching your cholesterol, that’s something to think about. MCTs aren’t the same as long-chain fats, but moderation’s still key.
MCT oil also has a low smoke point, so don’t use it for high-heat cooking. It can break down and lose its benefits pretty quickly if overheated.
Exogenous ketones can mess with your electrolytes because the salts add extra sodium, potassium, or calcium. Overdoing it might make you dizzy or give you a headache, especially if you’re not drinking enough water.
Some people feel a bit inflamed or tired when they first try ketone supplements or start ketosis. Usually, your body adapts and these things fade. If you’re using these products a lot or have other health stuff going on, it’s a good idea to check in with your doctor.
Practical Applications and Usage Tips

MCT oil and exogenous ketones can both help with energy and fat loss—if you use them right. They work best alongside a low-carb diet and pretty balanced nutrition, not as a magic fix on their own.
How to Incorporate MCT Oil
MCT oil mixes right into daily meals and drinks. Most people start with 1 teaspoon per day and slowly work up to 1–2 tablespoons to avoid any stomach issues.
Adding it to coffee, smoothies, or fat bombs gives a quick energy lift and can help you stay in ketosis. It’s an easy way to sneak in some extra fuel, honestly.
It’s best for low- to medium-heat cooking. High heat? Not so much—MCT oil doesn’t hold up well and can break down.
If you’re cooking with higher temps, something like avocado oil is a better pick. No need to risk wasting good MCT oil.
MCT oil works great as a pre-workout energy source or even just for a mid-morning boost. Pairing it with a low-carb meal helps keep energy steady and hunger down.
Keep it in a cool, dark spot to preserve the quality. That way, you avoid oxidation and keep it fresh longer.
| Use | Recommended Amount | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Coffee or tea | 1–2 tsp | Morning |
| Smoothies | 1 tbsp | Pre/post-workout |
| Fat bombs | 1–2 tbsp | Snack or dessert |
How to Use Exogenous Ketones Effectively
Exogenous ketones are most helpful for short-term energy or when you’re just starting out with ketosis. They can take the edge off that fatigue and brain fog a lot of people feel at first.
A single serving (usually 10–12 g of ketone salts) mixed with water or a low-carb drink is typical. Taking them before workouts or while fasting can bump up blood ketone levels and sharpen focus.
Just keep in mind, exogenous ketones aren’t a substitute for a low-carb diet. They’re more like a temporary fuel boost.
Drinking plenty of water helps with any side effects, like stomach upset or salt imbalance. It’s good to be cautious here.
Best to use them strategically—before tough workouts or mentally demanding tasks, not just at random.
Which Is Better for Energy and Fat Loss?

MCT oil and exogenous ketones both raise ketone levels, but they don’t work quite the same way. MCT oil supports steady energy and fat metabolism, while exogenous ketones give a fast, short-lived boost—handy during keto transitions or before a workout.
If your goal is long-term fat adaptation and consistent fat loss, building a structured keto plan is more important than choosing between individual supplements. MCT oil and exogenous ketones can support energy, but they cannot replace a properly designed macronutrient strategy.
If progress still feels inconsistent despite using tools like MCT oil or ketone supplements, it may be worth reviewing common structural mistakes that prevent fat loss on keto.
Choosing Based on Your Goals
If you’re after sustained energy and fat loss, MCT oil usually comes out ahead. It’s converted into ketones in the liver pretty quickly, helping you stay in ketosis and burn fat for fuel.
This supports metabolic health by nudging your body to rely on fat instead of carbs. MCT oil might also help curb appetite, which makes managing calories a bit easier.
But remember, it’s calorie-dense, so don’t go overboard. Portion control actually matters here.
If you need rapid energy for a workout or a mentally demanding task, exogenous ketones might be better. They raise blood ketone levels fast, no need to eat more fat, but the effect fades quicker than MCT oil’s energy.
| Goal | Better Option | Benefit Type |
|---|---|---|
| Steady energy | MCT oil | Long-lasting fuel |
| Quick boost | Exogenous ketones | Fast but short energy |
| Fat loss support | MCT oil | Promotes fat metabolism |
Combining MCT Oil and Exogenous Ketones
Some people use both to balance immediate and extended energy. MCT oil keeps ketone production steady, while exogenous ketones kick in fast when energy drops.
This combo can help maintain focus during tough workouts or fasting. For example, you might add MCT oil to your morning coffee, then take exogenous ketones before a workout for an extra push.
Together, they might make ketosis smoother and cut down on fatigue. It could also help with weight loss by improving fat use and keeping hunger at bay between meals.
Adjust the amounts to fit your own tolerance and energy needs—nobody wants digestive trouble from overdoing it.
Frequently Asked Questions

MCT oil and exogenous ketones each have their own impact on energy, fat metabolism, and ketosis. How you use them—timing, dose, everything—can really change how well you adapt to or stick with keto.
What are the primary differences between MCT oil vs exogenous ketones?
MCT oil comes from natural sources like coconut or palm kernel oil, helping your body make ketones on its own. Exogenous ketones are lab-made supplements that raise blood ketone levels directly.
MCT oil keeps ketone production and fat metabolism going, while exogenous ketones offer a faster, but temporary, rise in ketones.
How do MCT oil and exogenous ketones impact energy levels differently?
MCT oil gives steady energy by turning medium-chain fats into ketones through the liver. This is great for endurance and staying focused.
Exogenous ketones are more of a quick jolt—the body can use them right away, but the effect doesn’t last as long as what you get from MCT oil.
Can combining MCT oil with exogenous ketones enhance fat loss results?
Using both can help with fat loss by supporting ketosis and cutting down on hunger. MCT oil helps your body burn stored fat, while exogenous ketones may help keep your energy up when you’re eating less.
Sticking to ketosis is easier with both, but real results depend on your whole diet and activity level.
Are there specific times when one should prefer MCT oil over exogenous ketones, or vice versa?
MCT oil is good for daily use—morning or before a workout—to keep energy and mental clarity up.
Exogenous ketones are handy before tough exercise, during travel, or if you’ve eaten more carbs than planned and want to bounce back into ketosis quickly.
What are the potential side effects of using MCT oil compared to exogenous ketones for weight management?
MCT oil can cause stomach discomfort, cramping, or diarrhea if you take too much. Starting small helps avoid these problems.
Exogenous ketones might cause nausea or digestive upset, especially on an empty stomach or in high doses.
How do MCT oil and exogenous ketones fit into a ketogenic diet for optimal performance?
MCT oil supports natural ketosis and gives you a steady, fat-based energy source for both body and mind.
Exogenous ketones can help you stay in ketosis after slipping up or recover faster after workouts. If you use them right, both can fit into a solid ketogenic plan.
Conclusion

So, here’s the thing: MCT oil and exogenous ketones both play a role in energy and fat metabolism, but they’re not the same. MCT oil nudges your body to make its own ketones, while exogenous ketones just hand them over, no waiting around.
MCT oil usually gives a steadier energy boost because your liver breaks it down over time. Exogenous ketones? They spike your blood ketone levels fast, but that effect doesn’t really stick around.
| Supplement | How It Works | Energy Duration | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCT Oil | Converts to ketones in the liver | Sustained | Daily energy and fat metabolism |
| Exogenous Ketones | Adds ketones directly to the bloodstream | Short-term | Quick boost or keto transition support |
Some folks like MCT oil for daily routines since it fits with natural ketosis and might help keep hunger in check. Others reach for exogenous ketones before a workout or when they’re just starting out with low-carb eating and want to dodge that tired, sluggish feeling.
Honestly, mixing both—if you don’t go overboard—can help balance out those quick hits of energy with something that lasts a bit longer. The “best” pick? That’s really up to your own goals, how your body reacts, and what you eat day-to-day.
If you’re not sure where to start or how much to take, talking to a healthcare professional can clear things up. They’ll help you figure out what fits your health and activity level, which is probably smarter than guessing.
Many people focus on supplements before fixing their overall keto structure. In reality, fat loss results depend more on proper macro balance and consistency than on adding ketone products.
If you want a structured keto plan tailored to your metabolism, Keto Creator provides a personalized approach designed to remove guesswork and improve consistency.
